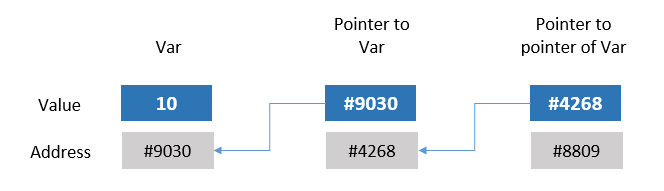
A pointer that points to another pointer is known as double pointer.
A pointer that contains the memory address of another pointer and that pointer contains memory adders of a variable of its type. Let’s understand it via a scenario, There are three people A, B, C . No one knows where does A & B live except C therefore if you want to meet A or B, first you will have to meet to C and ask for the location of B, Once you find out the location of B, you go to the location of B and ask for the location of A then you finally be able to meet to A. This same happens in computer memory, There is someone who knows the memory address of a pointer and that pointer has the memory address of a variable. Let’s look at the program.
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int A = 123; //a variable
int *B = &A; // pointer B that has address of A
int **C= &B; // double pointer that has address of pointer B
// <---------Some Code are described below---------->
return 0;
}
As a beginner we make mistake that we declare pointer and considered it as double pointer.
// int * C = &B ; // (Incorrect) This is still a pointer but not a double pointer .
Proper war to initialize is as using **(double Asterisk) than we assign address of a pointer .
int ** C = &B; //Correct
Application
Double pointer is heavily used at an embedded level so If you are Electronics or Electrical engineer you are going to notice it anyway. Let me explain one example…….

Have you wonder, how does your operating system get booted on a laptop even if you have multiple operating systems installed on a computer. So the point is Once firmware[A lightweight program installed by the manufacturer in FLASH which shows hardware level information] operation get completed and before giving control to the operating system , Firmware holds a double-pointer ,which first points to boot loader’s vector table[Generally at base Address of Vector table in ROM]
and at that vector table, there is an address to a structure. which has function and data address and using this function and data, booting sequence get started[Hardware checks are done and OS get started].
Subscribe for interesting stuff direct to your mail box.
NXP’s Kinetis KL13 series microcontroller, this Example code snippet is used to run bootloader:–
//May not exact but procedure is same
uint32_t runBootloaderAddress;
void (*runBootloader)(void * arg);
// Read the function address from the ROM API tree.
runBootloaderAddress = **(uint32_t *)(0x1c00001c);
runBootloader = (void ()(void * arg))runBootloaderAddress;
// Start the bootloader.
runBootloader(NULL);
// This is just for example use of double pointer.


Very well written Aditya! Looking forward to more posts!
LikeLiked by 1 person
NXP example is good enough to complex for beginner
LikeLike