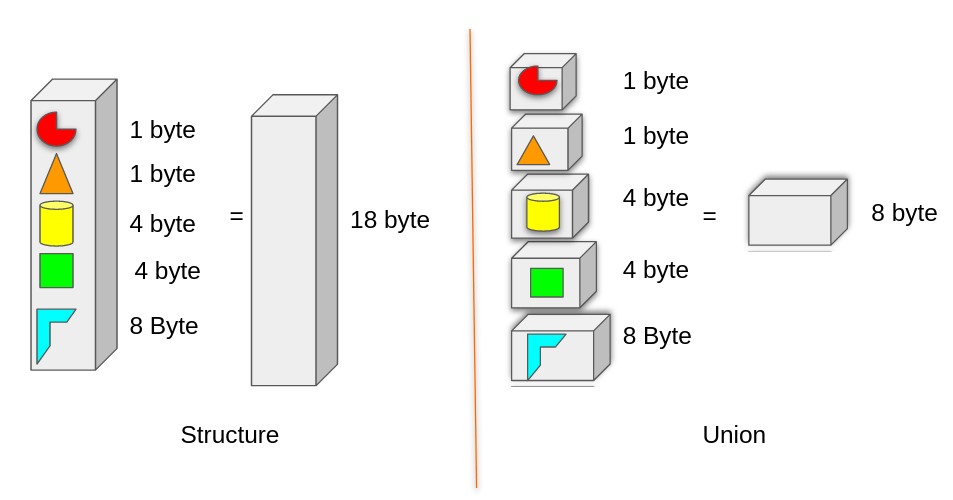
Structure and Union both are used to create a custom data type. As C language is a general-purpose, procedural computer programming language we often need functionality similar to OO language like C++. This is obtained through structure and interfaces.
Structure in C
Structure is used to create a custom data -type that a group of primitive ones. It is more like several data type element is packed and created into one data type.
Address of all member is different in memory.
Declaration
struct address
{
char name;
char street;
int city_id;
int state_id;
long description;
};
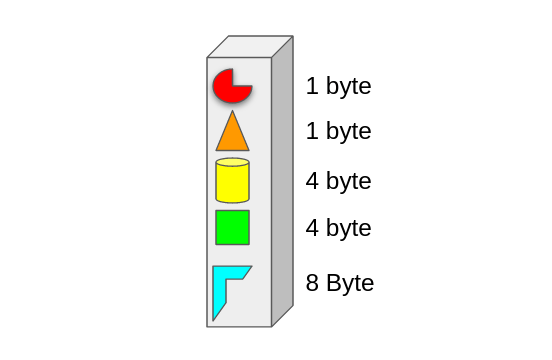

Size of structure
The size of the structure element is the combined size of all elements inside it. That will come to 18 bytes. You can test by the compiler.
#include<stdio.h>
struct address
{
char name;
char street;
int city_id;
int state_id;
long description;
};
int main(void) {
// your code goes here
struct address addr;
printf("%d\n",sizeof(address));
return 0;
}
Success #stdin#stdout 0s 5292KB
24
18 byte + 6 unused byte added by compiler for alignment in memory.
Union in C
Union is used to create a custom data type that is a union of all members declared into it. Basically A data type of minimum size that can hold a value of any kind of its member.
Address of all member is always same in memory.
Declaration
union address
{
char name;
char street;
int city_id;
int state_id;
long description;
};
Size of Union
Size of union is size of max size member.

#include<stdio.h>
union address
{
char name;
char street;
int city_id;
int state_id;
long description;
};
int main(void) {
// your code goes here
union address addr;
printf("%d\n",sizeof(addr));
return 0;
}


Leave a comment