A Table of pointers to virtual function is known as Virtual Table and pointer that point to that table is known as Virtual Pointer.
Each object is assigned a virtual pointer (vptr). This pointer points to a virtual table (vtbl). During initialization, the address of the virtual table is assigned to the virtual pointer. Let’s delve into the origin…
A Simple Object Model
The object model you mentioned operates like a table, where each member is indicated by a pointer within the table, rather than being directly present in the object’s creation. This approach allows for a more efficient use of memory and resources, as the object itself doesn’t need to contain all the members within its structure. Instead, it simply holds references to the location of each member, similar to how a table holds pointers to specific data. This method of handling object creation and member allocation is foundational to many programming languages and provides a versatile way to manage data and optimize system performance.
/**********************************************************
* Author :- Aditya Gaurav *
* Mail :- adiitrack7@gmail.com *
* *
* Please support https://www.errbits.com *
* Some content is taken for educational purpose credit to *
* The C++ Object model. *
*********************************************************/
@brief :- A simple object model in initial draft
class Point{
public:
Point(float xval);
virtual ~Point();
float x() const;
static int PointCount();
protected:
virtual ostream& print(ostream &os) const;
float _x;
static int _point_count;
};
Generated object Diagram
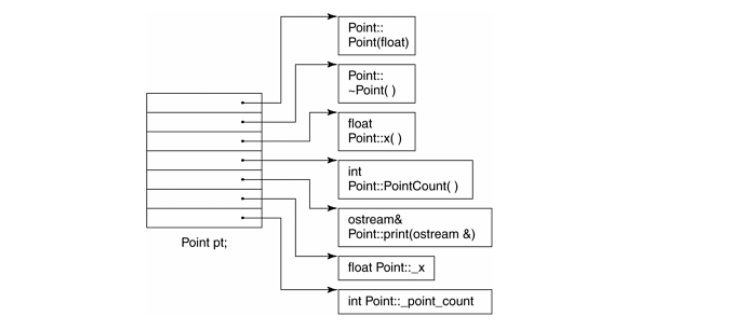
The table contains pointers to each member. This allows accessing each member using indexes, and the entries are initialized based on the class member declaration.
Table Object model
The model originates from the simple object model, but with a tweak: instead of a single table, two separate tables are used for data and function, and the object holds pointers to these two tables. This modification enhances data and function organization, leading to a more efficient system.
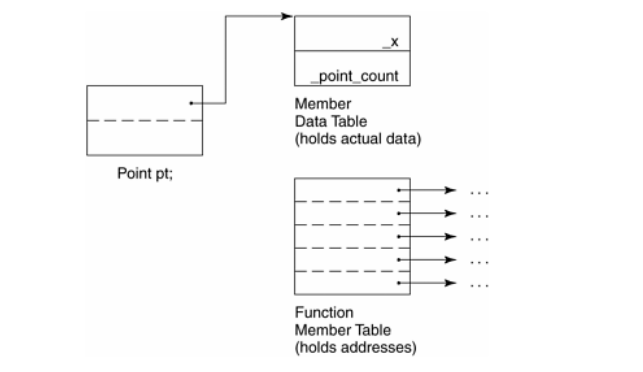
The C++ Object Model
This model is directly derived from simple object model where :-
- Non-static data member is directly placed into each object.
- Static data member is placed outside of object.
- Static and Non static member function is also place outside class object.
- Virtual function pointers are placed into a table(Virtual Table -4a) and a pointer( Virtual Pointer – 4b) to that table is placed into each class object.
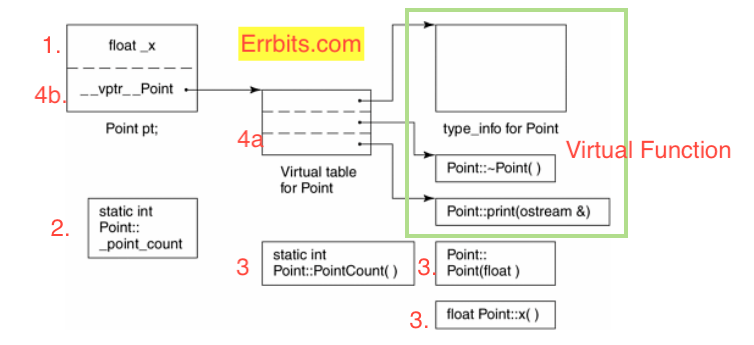
Bonus
- The handling of the virtual pointer is automatically done in the constructor, destructor, and copy assignment operator.
- If a class is derived, then a separate virtual table is made for the base class, and in this case, a separate pointer (bptr) is added to the object.
- This bptr is used to access the base class virtual table. So, for each virtual base class, a separate pointer is added to the object.
- bptr is often symbolized as __vptr__xxxx. xxxx refers to the class name.
One response to “Understanding C++ Object Model: Virtual Table and Virtual Pointer”
-
good explanation sir
LikeLike


Leave a comment